
Igo Etrich (1879 - 1967) and his 'Taube'
Taube - 1909 This early observation aircraft was called by the French, "the Invisible Aircraft". Because of the translucence of the clear doped linen covering the Taube was almost invisible when above 12OO feet. The world's very first "stealth plane"! It was one of the last WWI Scouts to use the wing warping method of control. The word 'Taube' means dove in German and you can see how it got it's name. Pretty easy to put together. The Austrian engineer Igo Etrich designed and flew his first tractor monoplane on 20 July 1909, and the first Taube prototype in July 1910. In late 1910 Etrich negotiated a manufacturing licence with Lohner in Austria and Rumpler in Germany, and the latter company produced most of the Tauben built from then until the outbreak of World War 1.
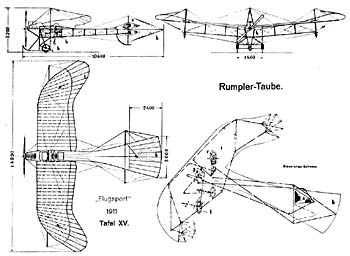 The Rumpler-Taube of 1911 Download a larger image
Those built from 1911 onward reflected a host of dimensional and other variations, but the 2-seat military version produced by Rumpler in 1912 was the most widespread and may be taken as typical. At the outbreak of war in Europe on 4 August 1914 Tauben were already in service with the air forces of Italy, Germany and Austro-Hungary as observation and training aircraft, and many later-famous German pilots learned to fly on aircraft of this type. Privately owned Tauben were impressed for military service, and a large-scale production programme was put in hand. By this time Dr. Etrich had relinquished his copyright in the design, following a dispute with Rumpler, and this left the way clear for Tauben for various types to be built in Germany by the A]batros, DFW, Gotha, Halberstadt, Jeannin, Kondor, Krieger, LVG, LilbeckTravemuinde and Rumpler factories. Etrich, meanwhile, joined forces with industrialist Gottfried Kruger in early 1914 to form the Braxidenburgische (later Hansa-und-Branden burgische) Flugxeugwerke GmbH. About five hundred Tauben were built in Germany, those by DFW and Jeannin being known as Stahltauben because of their steel-framed fuselages. A wide variety of engines, with output ranging from 70 to 120hp, were fitted to German-built machines, the most popular units being the Mercedes or Argus mimes of 100 or l2Ohp. The two versions in Austro-Hungarian service were the Lohner-built A. 1 (with 8Shp Austro-Daimler and overhead radiators) and the A. II (l20~ip Austro-Daimler with frontal radiator), built by Lohner and (as the Series 71 and 72) by the KuK. Flieger Arsenal at Fischamend. In August 1914 the Taube quickly proved its worth as a reconnaissance aircraft when it gave the Germans warning of a Russian advance during the Battle of Tannenburg. Later that month it was used for bombing when Lt. von Hiddesen dropped a small load of tiny bombs on Paris. The Taube was a stable aircraft with pleasant flying characteristics, and considering that it was already four years old when war broke out, its performance for 1914-15 was not at all bad. However, it was not highly manoeuvrable, and since it carried no armament other than crew members' revolvers or rifles), it was of little front-line value by the spring of 1915. It remained in use for a year or more thereafter as a very useful training type.
VOLUME XLII PART II.--MAY TO OCTOBER, 1915 THE CENTURY CO., NEW YORK FREDERICK WARNE & CO., LONDON PRACTICAL MECHANICS FOR BOYS http://home.earthlink.net
 Taube Monoplane at Rest, 1910
 Taube Monoplane in Flight, 1910
Igo Etrich und die berühmte 'Etrich Taube' Igo Etrich wurde 1879 in Trautenau geboren. Zuerst besuchte er die Oberrealschule und später die Handelshochschule in Leipzig. Nach Vollendung seines Lehrganges trat er in den Betrieb seines Vaters ein. Igo Etrich erfand die Schwingmaschine von Flachs und Hanf. Die Versuche Otto Liliensthals beeindruckten ihn stark. Er errichtete gemeinsam mit seinem Vater ein Versuchsatelier. Beide interessierten sich sehr für die Probleme der Stabilität. Etrich untersuchte auch Flügel von Vögeln und testete auch die Flugfähigkeit des Zanonia macrocarpa Samens, der auf Java wächst. 1903 baute Etrich ein Modell, mit dem er Gleitflüge bis zu 1 km schaffte. 1905 Bekam er ein Patent auf die Flügelform und Luftschraube. 1906 flog Franz Wels, ein Mitarbeiter Etrichs zum ersten Mal mit einem Gleitflügler. 1907 baute Etrich ein Motorflugzeug "Etrich 1". Bei diesem Flieger lag das Höhensteuer vorne und der Propeller hinten, doch der 24 PS-Motor war eindeutig zu schwach! Er verbesserte das Flugzeug, indem er die Luftschraube nach vorne versetzte und die Tragflügel zur Steuerung beweglich machte. Das Flugzeug hieß "Praterspatz". Er selber führte mit diesem Flugzeug Versuche durch. In der Ebene von WR. Neustadt ließ er zwei Hangars errichten. Im Juli 1909 gelangen ihm Gleitflüge bis zu 100 m . Auch Franz Bömisch und Karl Ilner waren gute Konstrukteure, später auch berühmte Flieger. 1910 hatte Karl Ilner seine Pilotenprüfung absolviert. Igo Etrich hatte seine "Etrich 1" verbessert indem er die Knüppelsteuerung durch einen Schwinghebel mit Volant ersetze, die zur Betätigung der "Verwindung" diente. Das Seitensteuer wurde mit den Füßen verstellt und sie wurde auch mit einem 40 PS-Motor ausgestattet. Schließlich fiel Igo Etrich im Dezember 1909 einem tragischen Unfall zum Opfer, war aber dennoch das Vorbild der neuen Type "Etrich 2"!
Taube : internetmodeler.com The most common 'German' aircraft of the immediate prewar, and early WWI years was not German in origin, but rather Austrian. Designed by Igo Etrich, the 'Taube' took its name - 'Dove' - from its birdlike appearance. As well as being built by Etrich, the Taube was constructed by many other firms in Germany and Austro-Hungary. The model depicted in the kit is of the first German aircraft to fly over Paris, the D-2 flown by A Friedrich and Dr. H Ellis flew from Berlin to Paris-Villacoublay on 7 September 1913. Later, with Etrich himself replacing Dr.Elias, they continued the trip from Paris to London on 13 September. The return journey from London to Berlin - via Calais, Antwerp, Nijmegan and Hannover - was undertaken from 17 September to 20 September 1913. The flight became immortalized as the "Five Countries Flight".
Taube : Luftwaffenmuseum, Berlin-Gatow The Taube (pidgeon) was designed by Austrian Igo Etrich. After turning out to be a successfull design it was build in large scale production by Rumpler in germany. It becam the first german military aircraft to be used in larger scales.
The Taube : Semad.Modelbouw
Taube : Poster for the Etrich Monoplan, 1911
|
© Copyright 1999-2002 CTIE - All Rights Reserved - Caution |